Formulation and evaluation of orally disintegrating tablet of metoclopramide hydrochloride
Abstract
Orally disintegrating drug delivery is currently the gold standard in the pharmaceutical industry where it is regarded as the fastest, safest, convenient, and most economic method of drug delivery having the highest patient compliance and preferred over conventional tablets. The goal of this study was to formulate and evaluate oral disintegrating tablets (ODTs) of Metoclopramide hydrochloride to overcome swallowing difficulties. The key to developing successful ODT formulation by direct compression method is to select the right super disintegrant. Nine formulations were prepared using different super disintegrants such as sodium starch glycolate (SSG), croscarmellose sodium (CCS), and crospovidone (CP) at three concentrations i.e. 2.8 %, 4 %, and 4.8 %. The formulation was evaluated for pre and post-compression parameters like angle of repose, compressibility index, Hausner's ratio, uniformity of content, thickness, hardness, friability, drug content, wetting time, water absorption ratio, dispersion time, in-vitro disintegration time etc. Results revealed that among the 9 formulations, the formulation MHF9 containing 4.8 % of crospovidone was selected as the best formulation as its wetting time 28 second, disintegration and dispersion time 7 second and 18 seconds respectively, percentage drug release after 15 minutes was 102.52 %.
Keywords
Formulation, orally disintegrating tablets, metoclopramide hydrochloride, direct compression, superdisintegrants
INTRODUCTION
Recent progress in novel drug delivery system aims to improve the safety and efficacy of the drug molecule by formulating a dosage form being for the administration. A solid dosage form that dissolves or disintegrates rapidly in the oral cavity, resulting in solution or suspension without the need for water is known as orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs). These are newer types of tablets that break up in saliva within a few seconds. Oral disintegration tablets offer some advantages over conventional tablets 1.
Dysphasia is a common problem encountered in all age groups, especially the elderly and pediatrics because of physiological changes associated with those groups. In concerned to oral solid dosage form such problems consequences in a high occurrence of noncompliance and unproductive therapy. Nowadays, increasing consideration have be remunerated to formulate not only rapid disintegrating tablets to facilitate are swallow but also orally decomposed tablets that are intended to disintegrate rapidly in the mouth. ODTs offer an advantage for the population who have difficulty in swallowing conventional tablets or capsules, bedridden, mentally sick, and uncooperative patients suffering from nausea, motion sickness, sudden episodes of allergic attack, or coughing 2. The major benefits of such dosage form, in terms of patient compliance, rapid onset of action, increased bioavailability, good stability, and good flavor enhance the suitability of bitter tasting drugs that make these tablets popular as a dosage form of choice in the current market 3.
The basic approach used in the development of an oral disintegration tablet is the use of super disintegrants. Due to the presence of super disintegrants, it gets dissolved quickly, resulting in rapid absorption of drugs which in turn provides rapid onset of action. Since absorption takes place directly from the mouth and avoids the first-pass metabolism, so bioavailability of the drug increases. There are various natural disintegrants like gum karaya, modified starch, agar, and synthetic disintegrants like microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, croscarmellose sodium, sodium starch glycolate, etc. which have been used in the formulation of fast dissolving tablets at concentration range up to 10 % by weight relative to the total weight of dosage form4.
In the modern history, numerous techniques cover for the development of orodispersible tablets such as freeze drying or lyophilization, spray drying, molding, sublimation, mass extrusion, and direct compression 5. Due to low manufacturing costs, conventional pieces of equipment, and a few number of processing steps lead this direct compression technique to be a preferable way to manufacturing orodispersible tablets 4.
Metoclopramide hydrochloride is a free water-soluble clinically potent antiemetic and gastro-prokinetic drug effective for the prevention of different types of emesis. Its conventional dosage form such as tablet and solution give poor bioavailability due to extensive first-pass metabolism6, 7. In addition to its bitter taste, difficulty swallowing tablets or nausea/vomiting may reduce patient adherence to therapy. The newly developed formulations should try to diminish the patient noncompliance and improve palatability.
In the present study, we attempted to formulate and evaluation of an orodispersible tablet of Metoclopramide HCl that was manufactured through a direct compression technique using cross carmellose sodium, sodium starch glycolate, and crospovidone as super disintegrants. The study aimed to assess the effect of the super disintegrants on wetting time, dispersion time, and disintegration time profile of the orodispersible tablets.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The study was carried out in the year 2017 at the Pharmaceutics laboratory at Asian College for Advance Studies (ACAS), Lalitpur, Nepal.
Materials
Metoclopramide hydrochloride (an active pharmaceutical ingredient) and super disintegrant agents such as cross carmellose sodium (CCS), sodium starch glycolate (SSG), and cross povidone (CP) was obtained from Chemi Drug Industries Pvt. Ltd. Kathmandu, Nepal. Each super disintegrant was tested at 2.8 %, 4 %, and 4.8 % concentrations using the maximum concentration as mentioned in the Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients. Mannitol and microcrystalline cellulose PH 102 were used as a binding and filling agent. The vanilla and sodium saccharin was use as a flavoring and sweetening agent. Talc and aerosol were used as lubricant and magnesium stearate as a glidant. All the excipients used in this research were pharmaceutical grade.
Methods
Drug-Excipient Compatibility Study
In this study, each of 50 mg of active pharmaceutical ingredient (i.e. Metoclopramide HCL) and the other formulation excipients were mixed in 1:1 ratio in different vials. 10 excipients were taken in different vials and active drug was added in each. All these experiments were performed three sets. Then, above vials were stored as follows for checking drug-excipients interactions.
-
Normal room temperature conditions, i e 25oC and 60% relative humidity, plugged.
-
Accelerated temperature conditions, i.e. 40o C and 75% relative humidity, both plugged and unplugged conditions.
For maintaining this above condition, humidity chamber was used 8. It was checked for physical compatibility (state, color, and odor) in interval of 7 days for a month.
Preparation of orally disintegrating tablets
Orally disintegrating tablets of Metoclopramide HCL were manufactured through the direct compression technique. A batch of 150 tablets was prepared for all the designed nine formulations and detail of the components of the formulation as mentioned in Table 1. All the excipients and active pharmaceutical ingredients with proper quantities were sieved through mesh # 80 separately. Firstly, Metoclopramide hydrochloride and super disintegrants were mixed properly. Mannitol and microcrystalline cellulose PH 102 were mixed separately followed by sodium saccharin and vanilla flavor. After that aerosol, magnesium stearate and talc were mixed. At last, the mixed powder was blended in the polythene bag. Finally, the resultant final blend was directly compressed into tablets using 12 station rotary press machines with a 10 mm diameter flat round shape punch. Before tablet preparation, the entire powder blends were evaluated for the following pre-formulation parameters 9, 10.
Evaluation of pre-formulation parameter
The angle of repose (θ)
The angle of repose (θ) was determined according to the free standing cone funnel method. The accurately weighed granules or blend was allowed to flow through the funnel freely onto the graph paper, until its apex and the funnel tip touches each other, till a highest heap height (h) was obtain. The radius (r), of the granule or powder heap, was calculated and the angle of repose was computed using the following equation:
Bulk density (δb)
0) and weight of the granules (W) were taken “as it is”.
Tapped density
f) occupied in the cylinder and the weight (W) of the blend was measured. The tapped density was calculated using the following formula.
Compressibility index (CI)
Hausner’s ratio
Evaluation parameter of formulated tablets
All the formulated tablets were undertaken for the following parameters.
Physical appearance
Dimensional analysis
Breaking force or Hardness
2) 11.
Friability (F)
12.
Where, W1:- Tablets weight before friability.
W2:- Tablets weight after friability.
Weight variation
Wetting time
13.
Water absorption ratio
13.
The water absorption ratio ‘R’ was determined using the equation,
Where, Wa = Tablet weight after water absorption.
Wb= Tablet weight before water absorption.
Dispersion time
In-vitro disintegration time
16.
Uniformity of content
17.
Assay of tablets
17.
RESULTS
Drug-Excipient Compatibility Study
All the drug-excipient stored vials were inspected physical state for a month. Physical state, color, and odor of drug-excipient mixture were compatible in both normal room temperature and accelerated temperature conditions. Since, all excipients were appropriate for formulation of Metoclopramide HCl oral disintegrating tablets.
Table 1 revealed the details of the components of the formulation of Metoclopramide hydrochloride ODT.
|
S.no. |
Ingredients (mg/tablet) |
MHF1 |
MHF2 |
MHF3 |
MHF4 |
MHF5 |
MHF6 |
MHF7 |
MHF8 |
MHF9 |
|
1. |
Metoclopramide HCl |
10.57 |
10.57 |
10.57 |
10.57 |
10.57 |
10.57 |
10.57 |
10.57 |
10.57 |
|
2. |
Sodium starch glycolate |
7 |
10 |
12 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
3. |
Crosscarmellose sodium |
- |
- |
- |
7 |
10 |
12 |
- |
- |
- |
|
4. |
Crospovidone |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
7 |
10 |
12 |
|
5. |
Microcrystalline cellulose pH 102 |
158.43 |
155.43 |
153.43 |
158.43 |
155.43 |
153.43 |
158.43 |
155.43 |
153.43 |
|
6. |
Sodium saccharin |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
7. |
Magnesium stearate |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
8. |
Mannitol |
50 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
50 |
|
9. |
Flavor (vanilla) |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
|
10. |
Talc |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
11. |
Aerosil |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
|
Total wt. (mg) |
250 |
250 |
250 |
250 |
250 |
250 |
250 |
250 |
250 |
Evaluation of pre-formulation parameter
The results revealed that all formulation has good and fair flow properties. The angles of repose and compressibility index of all nine formulations were in the range of 30o to 35o and 18-23 respectively. MHF9 had the best angle of repose i.e., 30.11, and Compressibility index of 18 in comparison to other formulations. Thus, MHF9 shows the best flow property. The summary of the angle of repose, compressibility index, and Hausner's ratio is tabulated in Table 2 .
|
Formulation |
Angle of repose (In degree) |
Compressibility index (%) |
Hausner’s ratio |
|
MHF1 |
34.01±0.52 |
22.22±0.13 |
1.32±0.015 |
|
MHF2 |
34.21±0.50 |
20.98±0.10 |
1.30±0.014 |
|
MHF3 |
32.9±0.49 |
21.73±0.11 |
1.31±0.016 |
|
MHF4 |
34.0±0.51 |
23.0±0.15 |
1.31±0.013 |
|
MHF5 |
34.21±0.53 |
19.0±0.12 |
1.24±0.015 |
|
MHF6 |
34.22±0.52 |
21.42±0.17 |
1.27±0.019 |
|
MHF7 |
31.13±0.46 |
20.83±0.15 |
1.26±0.018 |
|
MHF8 |
31.79±0.47 |
20.0±0.14 |
1.25±0.015 |
|
MHF9 |
30.11±0.54 |
18.0±0.19 |
1.22±0.020 |
Evaluation parameter of formulated tablets
All the formulated tablets were subjected to general appearance and chemical evaluation. Entire formulated tablets with white color having flat face beveled edge round having standard bisect break line in one face and smooth face on another side. The average thickness and the average weight of the sample tablets from all formulation were found to be 3.03-3.07 mm and 237.32-263.10 mg, which was within the IP range as depicted in Table 3 .
|
Formulations |
Thickness (mm) |
Average wt. (mg) |
Dev.* |
||||
|
Tablet 1 |
Tablet 2 |
Tablet 3 |
Tablet 4 |
Tablet 5 |
|||
|
MHF1 |
3.01 |
3.00 |
3.013 |
3.02 |
3.06 |
249.83 |
237.37-262.32 |
|
MHF2 |
3.09 |
3.011 |
3.08 |
3.00 |
3.012 |
249.58 |
237.101-262.059 |
|
MHF3 |
3.00 |
3.014 |
3.014 |
3.019 |
3.016 |
250.51 |
237.50-262.51 |
|
MHF4 |
3.015 |
3.24 |
3.22 |
3.017 |
3.02 |
250.91 |
238.36-263.45 |
|
MHF5 |
3.019 |
3.00 |
3.011 |
3.00 |
3.014 |
250.16 |
237.65-262.66 |
|
MHF6 |
3.011 |
3.021 |
3.015 |
3.018 |
3.021 |
250.35 |
237.83-262.86 |
|
MHF7 |
3.022 |
3.016 |
3.00 |
3.00 |
3.013 |
250.58 |
238.01-263.1 |
|
MHF8 |
3.06 |
3.018 |
3.023 |
3.09 |
3.01 |
249.2 |
237.32-262.3 |
|
MHF9 |
3.09 |
3.01 |
3.016 |
3.017 |
3.017 |
250.25 |
237.73-262.76 |
The summary of diameter, hardness, friability, disintegration time, dispersion time, wetting time, water absorption ratio, content uniformity, and the assay is tabulated in Table 4 . The diameter of all the formulation was 10 mm. The hardness of the made-up formulation was optimum. Friability test results show that the entire formulation was mechanically stable i.e. was within IP 2010 range ≤1 % 17. Among all the formulation MHF2 has the best friability. The disintegration and dispersion time of all the formulations was within the range i.e. within 3 minutes as per IP 2010. Among them, MHF9 shows the best disintegration time and dispersion time of 7 sec and 18 sec respectively in which 4.8 % crospovidone was used. All the formulations were dispersed uniformly within the time and all the formulation was passed through 710 µm as per IP except MHF1, MHF2, and MHF3. So these three (MHF1, MHF2, and MHF3) do not comply with IP 2010 17. Among all the formulations, MHF9 showed the best wetting time i.e. 28 seconds. The uniformity of content and drug assay of entire formulation was within the limit (90% to 110%) as per IP 2010 17. Among all the formulation MHF9 shows the best uniformity of content and assay which was found to be 102.99 % and 102.91 % respectively.
|
Evaluation parameters |
Designed formulations |
||||||||
|
MHF1 |
MHF2 |
MHF3 |
MHF4 |
MHF5 |
MHF6 |
MHF7 |
MHF8 |
MHF9 |
|
|
Diameter (mm) Mean (n=5) |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
10 |
|
Hardness (kg/cm2) |
2.58 |
2.66 |
2.06 |
2.40 |
2.33 |
2.50 |
2.83 |
2.56 |
2.68 |
|
Friability (%) |
0.55 |
0.42 |
0.62 |
0.73 |
0.71 |
0.69 |
0.72 |
0.69 |
0.72 |
|
Disintegration time (sec)* |
30±0.31 |
35±0.40 |
20±0.30 |
28±0.28 |
24±0.29 |
19±0.28 |
15±0.26 |
10±0.27 |
7±0.25 |
|
Dispersion time (sec)* |
82±1.05 |
71±1.06 |
43±1.07 |
56±1.05 |
55±1.10 |
40±1.06 |
26±1.07 |
24±1.05 |
18±1.02 |
|
Wetting time (sec)* |
36.33±1.20 |
120±1.24 |
68.6±1.31 |
91.3±1.27 |
78±1.31 |
79±1.26 |
31±1.28 |
29.66±1.29 |
28±1.26 |
|
Water absorption ratio |
99.92 |
106.41 |
153.07 |
113.81 |
123.65 |
153.19 |
112.49 |
119.15 |
115.38 |
|
Uniformity of content (%) |
91.2 |
91.43 |
97.67 |
95.49 |
99.24 |
97.25 |
95.93 |
102.33 |
102.99 |
|
Assay (%) |
100.06 |
99.40 |
96.77 |
97.50 |
101.87 |
94.73 |
99.66 |
100.98 |
102.91 |
Comparative study of super disintegrants
Disintegration time
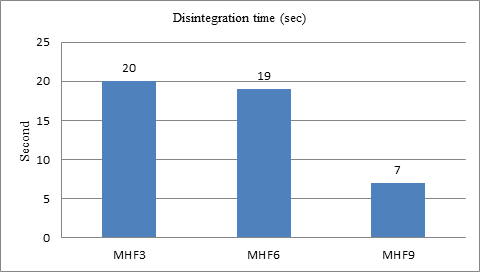
Comparing three super disintegrants sodium starch glycolate, croscarmellose sodium, and crospovidone in varying concentration, we found that crospovidone concentration (4.8 %) show the best disintegration than other two super disintegrants. Among all the three formulation prepared by using sodium starch glycolate, MHF1 (concentration 2.8 %), MHF2 (concentration 4 %), and MHF3 (concentration 4.8 %); MHF3 showed comparatively better disintegration time compared to the other two concentrations. Among the three formulation prepared by using Croscarmellose sodium, MHF4 (concentration 2.8 %), MHF5 (concentration 4 %) and MHF6 (concentration 4.8 %); MHF6 showed better disintegration time. Among three formulation prepared by using crospovidone, MHF7 (concentration 2.8 %), MHF8 (concentration 4 %) and MHF9 (concentration 4.8 %); MHF9 showed comparatively better disintegration time. These results are in line with the previous study conducted by Satpute et al., SSG, CCS, and CP were in use as super disintegrants for Metoprolol orally disintegration tablets formulation. In this previous study by satpute et al., the crospovidone (6.6 %) containing formulation show a better disintegration time 18.
Dispersion time
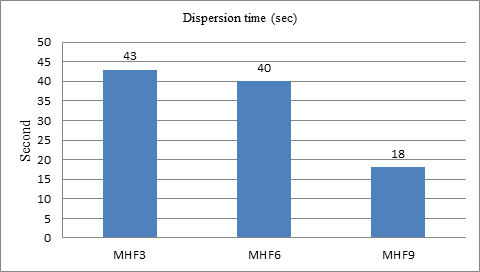
Comparing three super disintegrants sodium starch glycolate, croscarmellose sodium, and crospovidone in varying concentration, we found that crospovidone concentration (4.8 %) show the best dispersion time than other two super disintegrants. Among all the three formulation prepare by using sodium starch glycolate, MHF1 (concentration 2.8 %), MHF2 (concentration 4 %), and MHF3 (concentration 4.8 %); MHF3 showed comparatively better dispersion time compare to the other two concentration. Among the three formulation prepared by using Croscarmellose sodium, MHF4 (concentration 2.8 %), MHF5 (concentration 4 %) and MHF6 (concentration 4.8 %); MHF6 showed better dispersion time. Among three formulation prepared by using crospovidone, MHF7 (concentration 2.8 %), MHF8 (concentration 4 %) and MHF9 (concentration 4.8 %) showed comparatively better dispersion time. These results are in agreement with the study conducted by Hussam et al., CP was found to be the best super disintegrant with a concentration of 40 mg/tab 19.
DISCUSSION
The present research was undertaken to formulate the ODTs of Metoclopramide hydrochloride through direct compression technique with various super disintegrant with various concentrations and keeping other excipients the same. Three different super disintegrants were used i.e. croscarmellose sodium, sodium starch glycolate, and crospovidone. The primary requirement for all the dosage forms is to disintegrate quickly. A total of nine formulations were prepared and evaluate the pre-formulation parameters like bulk density, tapped density, angle of repose, compressibility index, and Hausner's ratio. The formulated tablets meet the pharmacopeia requirements of the angle of repose, compressibility index, and uniformity of weight, friability, disintegration time, dispersion time, and uniformity of dispersion as per IP 2010. All the pre-formulation studies were found within prescribed limits and indicated well to fair free-flowing nature. Each drug-excipients mixture was found to be compatible for a month. Values for an angle of repose were found in the range of 30.11° to 34.22° showing that the blend of powder was free-flowing and can be used for direct compression. The value of compressibility index was found in the range of 23 to 22.22, demonstrating that entire batches of tablet granules have good flow ability properties. Hausner's ratio was found to be in the range of 1.32 to 1.22 also indicates good flow properties. The breaking force of tablets was found to be in the range of 2.3 to 3.03 kg/cm2. Friability was observed between 0.42 to 0.73 %. Thus the hardness and friability data indicate good mechanical resistance of tablets. The tablet thickness of all nine formulations varied from 2.98 mm to 3.041 mm. The average weight of the tablet is 250 mg. According to IP 2010, the % deviation weight of 250 mg or more tablets is ± 5%, so the range is 237 to 263.45 mg. The sample tablets from all the formulations were within the range. In-vitro disintegration time for different batches ranges from 7 (MHF9) to 35 (MHF2) seconds. This was one test to be considered to select one best formulation from nine formulations. According to this test, MHF9 is the best formulation as it showed the lowest time for disintegration i.e. 7 sec., when the amount of super disintegrants crospovidone increases up to 4.8% per tablet, the disintegration time decrease. Wetting time is determined to get the idea of wetting lag time before disintegration and also found that as the wetting time decreased disintegration time also decreased. Wetting time is directly proportional to the Dispersion time, when the wetting time of tablets was deceased, increases the dispersion time of the tablets. The wetting time value of this test ranges from 28 (MHF9) to 120 (MHF2) sec. Dispersion time of all the formulations was within the range i.e. within 3 min as per IP (2010). Among them, MHF9 Shows the best dispersion time of 18 sec in which 4.8 % crospovidone was used. Dispersion time of all the formulations was complying with IP but in case of MHF1 and MHF2; dispersion time is longer than other formulations. Dispersion times of these two formulations (MHF1 and MHF2) is longer due to SSG which is nonporous in nature and are exaggerated via the presence of hydrophobic excipients and lubricating agents. Since crospovidone and croscarmellose sodium showed better dispersion as well as disintegrating time than SSG. This may be due to rapid capillary and swelling action. Thus these results indicate that these tablets would disintegrate almost instantaneously when they will come in contact with even a slight quantity of saliva in the mouth. The formulation (MHF9) having 4.8 % of crospovidone showed the best results when compared to other formulations. In a previous study done by Mohanachandran, the disintegration time was reduced to 21 sec on increasing the concentration of CP 20. CP provides the best overall sensory experience as well as rapid disintegration and robustness 4. Thus the liberating rate of Metoclopramide HCl was significantly enhanced by formulating ODT using CP as a super disintegrating agent. Its assay was obtained 102.91 %, disintegration, and dispersion time was obtained 7 sec and 18 sec respectively. Among all the formulations containing different concentrations of Croscarmellose sodium, Crospovidone, and Sodium starch glycolate; formulation MHF9 containing Crosspovidone of 4.8 % shows better dispersion as well as disintegration time than Crosscarmellose and Sodium starch glycolate. This may be due to the rapid capillary and swelling action of Crosspovidone. Hence, these finding revealed that disintegration time can be minimize through using a wicking type of super disintegrating agent such as Crospovidone 18.
CONCLUSION
Oral disintegrating tablets of Metoclopramide hydrochloride can be successfully prepared by direct compression techniques using three super disintegrants i.e., sodium starch glycolate, crospovidone, and croscarmellose sodium. The ODTs prepared by using crospovidone (4.8 %) by direct compression is more efficient by the evaluation parameter (disintegration time, dispersion time, and wetting time) concerning other super disintegrants (SSG and CCS). In conclusion, the orally disintegrating tablets of Metoclopramide hydrochloride would be quite effective in emetic patients by providing rapid onset of action without the need for water during the administration. The overall rank order of disintegrating ability among disintegrants used was found to be CP > CCS > SSG.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are thankful to Chemi-Drug Industries, Pvt. Ltd., Kathmandu, Nepal, for providing us active and others excipients and allowing for study drug-excipients interaction. Also, we would like to thank the Department of Pharmacy, Asian College for Advance Studies, Lalitpur for their supporting throughout the research.CONFLICT OF INTEREST: Nil.